The Comprehensive Guide to Types of Mutual Funds in India

 Jun 17, 2024
Jun 17, 2024 8 Mins
8 MinsIn India, mutual funds can be categorized based on structure, asset class, and investment objectives, also accounting for investors’ risk appetite. Here, we explore the varied types of mutual funds.
Mutual Fund Types Based on Structure
Mutual funds are classified as open-ended, close-ended, or interval schemes based on their maturity period. Let's delve into each type:
Open-ended Mutual Funds
Open-ended mutual funds offer investment flexibility, allowing investments and redemptions at any time without a maturity period. They are typically highly liquid. Most mutual funds fall under this category, except for ELSS and some solution-oriented schemes, which have lock-in periods.
Close-ended Mutual Funds
These funds have a fixed investment and maturity period, accessible only during the New Fund Offer (NFO). Post-NFO, these funds may be listed on stock exchanges, enabling trades as per SEBI guidelines requiring exit routes.
Interval Mutual Funds
As implied by their name, interval mutual funds permit transactions only at designated intervals and function like close-ended funds with timed windows for entry and exit.
Mutual Fund Types Based on Asset Class
Depending on where they invest, mutual funds classify as:
Equity Mutual Funds
Equity funds allocate capital to company stocks, with returns tied to market performance. Although high-risk, they can yield substantial returns. These funds must hold a minimum of 65% in equities, covering types like large-cap, mid-cap, and sectoral funds.
Debt Funds
Debt funds invest in fixed-income assets like corporate and government bonds, focusing on generating income through interest and capital appreciation, offering stability with some risk.
Hybrid Mutual Funds
Hybrid funds mix debt and equity investments to balance long-term growth and short-term stability. Instances include multi-asset allocation and balanced advantage funds.
Based on Investment Objectives
Mutual funds also align with specific investment goals:
ELSS Funds
ELSS funds provide equity returns with tax benefits under Section 80C, subject to a 3-year lock-in.
Liquid Funds
These debt funds prioritize capital safety and stable returns by investing in short-term debt securities, ideal for flexible short-term investments.
Capital Protection Funds
Focusing on principal security, these funds primarily invest in debt while allocating partly to equities for growth prospects.
Fixed-Maturity Plans
FMPs are fixed-term, closed-ended debt investments aligned with the scheme’s maturity, catering to risk-averse, short-term investors.
Pension Funds
Designed for retirement, these funds have extended lock-in periods, investing in varied asset classes to accumulate a retirement corpus.
Income Funds
Primarily debt-focused, income funds target wealth accumulation through capital appreciation and dividends.
Growth Funds
Aim for capital enhancement by investing in growth-centric companies; these are suitable for bold investors ready to take on high risk.
Money Market Funds
Investing in low-risk, short-term debt, these funds offer superior returns for surplus funds, safer than traditional bank deposits.
Fund of Funds (FoF)
By investing in other mutual fund schemes rather than individual securities, FoFs provide diversification.
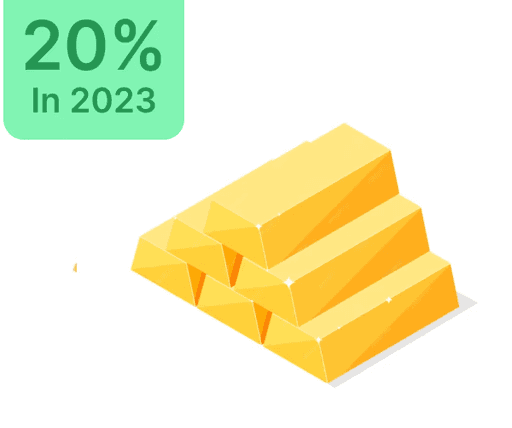
Gold Funds
Gold funds align with gold ETFs, protecting against inflation as part of a diversified portfolio.
Based on Portfolio Management
- Active Mutual Funds: Fund managers actively manage portfolios for optimum returns through strategic buying and selling.
- Passive Mutual Funds: These funds follow a specific index, maintaining compositions mirroring the index.
Based on Specialty
- Sectoral Funds: Focus at least 80% on a specific economic sector such as pharma or technology.
- Index Funds: These mimic an underlying index's performance through proportionate stock holdings.
- Real Estate Funds: Invest in equities within the real estate sector, concentrating on the sector's companies.
- Asset Allocation Funds: Also termed Balanced Advantage Funds, dynamically invest in stocks and debts based on market trends.
- International Funds: Offer geographical diversification by investing in foreign-listed companies.
- Global Funds: Invest globally, excluding the investor's home market.
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs): Trade like stocks in real-time, aligning with indices or commodities like gold.
Based on Risk Appetite
- Low-Risk Funds: Invest in quality bonds for steady growth with minimal risk, such as liquid and ultra-short duration funds.
- Medium-Risk Funds: Balance risk and return, typically via hybrid schemes spanning multiple asset classes.
- High-Risk Funds: Suitable for those accepting volatility, like pure equity funds, targeting higher returns.
Conclusion
India offers diverse mutual fund types catering to varied investor preferences and risk levels. To choose suitable schemes, evaluate your financial goals and investment horizons. A diversified mutual fund portfolio can help balance risks and optimize returns effectively.