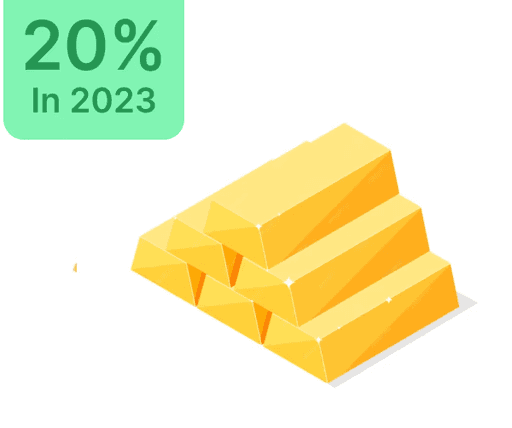
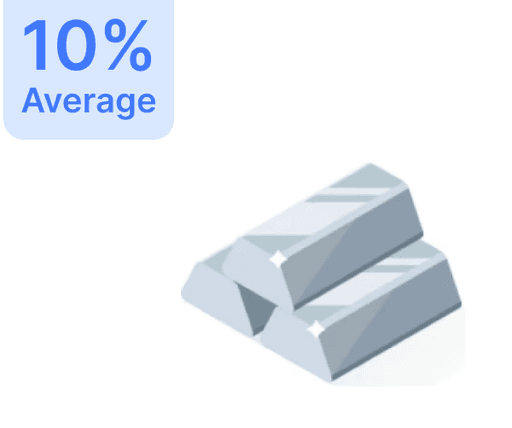
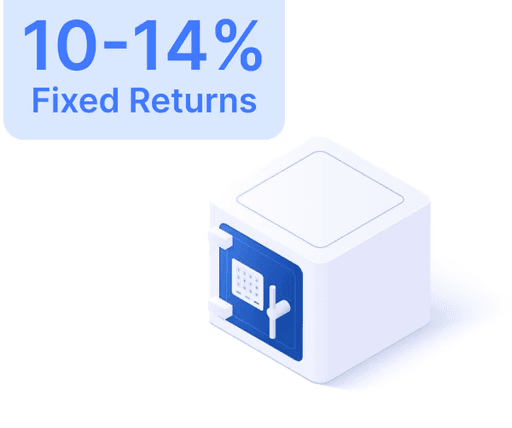
What is SEBI's Role in India's Securities Market?

 Jun 14, 2024
Jun 14, 2024 7 Mins
7 MinsThe Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) serves as the regulatory entity for the Indian securities market, officially established on April 12, 1992, under the SEBI Act 1992.
What is SEBI?
SEBI, a statutory body of the Indian Government, was created on April 12, 1992, to ensure transparency and fairness in India's investment market. The headquarters of SEBI is located in Mumbai, with regional offices in New Delhi, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, and Chennai.
History of SEBI
Prior to the formation of SEBI, India's securities market was regulated by various government institutions, which resulted in inconsistencies and inefficiencies. In 2014, SEBI received enhanced regulatory powers from the Indian government, enabling it to execute search and seizure operations and impose more stringent penalties for market manipulation and insider trading. Today, SEBI is recognized globally as a leading regulatory authority, significantly influencing the development and regulation of the Indian securities market.