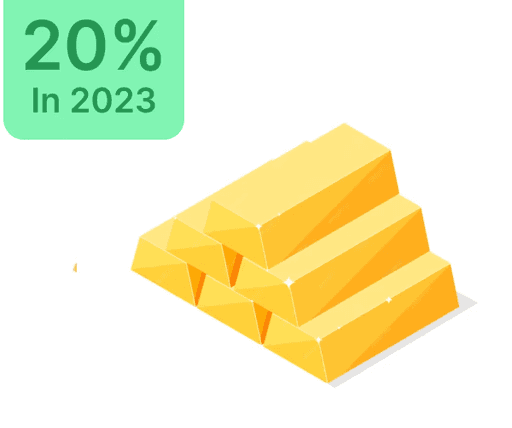
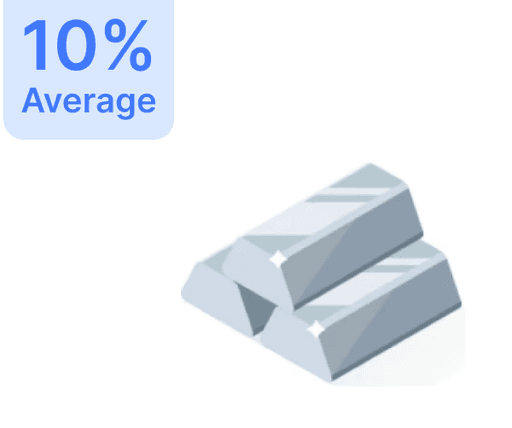
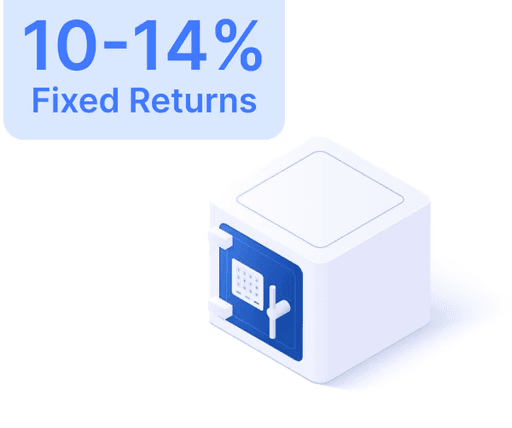
Understanding Large-Cap Stocks: The Stable Investment Choice

 May 10, 2023
May 10, 2023 5 Minutes
5 MinutesLarge-cap stocks, also known as large-capitalization stocks, are shares issued by companies with significant market capitalization. This is calculated by multiplying the total number of shares by the current share price, and it serves as a critical metric for evaluating a company's overall worth.
Comprehending Large-Cap Stocks: The Bedrock of Stability
Companies classified as large-cap are generally identified by their financial maturity and stability, establishing them as integral to the stock market. Despite offering moderate returns compared to mid-cap and small-cap stocks, their unparalleled stability and lower risk make them essential for a diversified investment portfolio.
Main Attributes of Large-Cap Stocks: Understanding Their Nature
Moderate Returns and Dividends:
Large-cap stocks tend to generate moderate returns, primarily through consistent dividends.
Low Risk and Resilience:
With robust financial underpinnings, large-cap companies are less affected by market fluctuations, reducing risks for investors.
Established Operational History:
These companies exhibit a long operational history, which adds to their transparency with easily accessible financial documentation.
Higher Valuation:
They usually come at a higher cost, representing market leadership and quality.
High Liquidity:
A broad popular appeal leads to high liquidity for large-cap stocks in the market.
Stock Exchange Integration:
Globally, major indices often feature large-cap stocks prominently. In India, the Nifty 50 index showcases the top fifty large-cap stocks.
Pros and Cons of Investing in Large-Cap Stocks: Evaluating the Balance
Benefits:
Stability Amid Market Volatility:
During market instability, large-cap stocks serve as a stable anchor, fostering resilience in investment portfolios.
Consistent Income from Dividends:
Providing a primary income stream, dividends from large-cap stocks ensure steady cash flow.
Transparency in Financial Statements:
Large-cap companies typically adhere to transparency standards, offering investors easy access to financial data.
Drawbacks:
Limited Potential for Capital Appreciation:
The opportunity for capital growth is often lower compared to mid-cap and small-cap stocks.
Significant Capital Requirement:
Requiring substantial investment outlay, large-cap stocks may present affordability issues for those with restricted disposable income.
Exploring Options: Diversification and Beyond
Mid-Cap Stocks:
Higher chances for capital appreciation but with increased volatility.
ETFs and Equity Funds:
These provide stock-like features and diversification for a balanced investment strategy.
Multibagger Stocks:
These can offer significant returns for those looking for alternative growth opportunities.
Guidance for Strategic Decisions:
Engaging with market specialists or using trusted investment platforms is recommended before investing. Evaluating personal investment goals, feasibility, and affordability are key components of making informed decisions within the variable domain of large-cap stocks and alternatives.